
Int Pediatr 10: 51–56.ĭesjeux J-F, Turk E, Wright E (1995) Congenital selective Nà D-glucose cotransport defects leading to renal glycosuria and congenital selective malabsorption of glucose and galactose.
N Engl J Med 325: 703–709.ĭe Vivo DC, Garcia-Alvarez M, Ronem G, Trifiletti R (1995) Glucose transport protein deficiency: an emerging syndrome with therapeutic implications. J Biol Chem 255: 4758–4762.ĭe Vivo DC, Trifiletti RR, Jacobson RI, Ronen GM, Behmand RA, Harik SI (1991) Defectiveglucose transport across the blood-brain barrier as a cause of persistent hypoglycorrhachia,seizures and developmental delay. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 4088–4092.Ĭushman SW, Wardzala LJ (1980) Potential mechanism of insulin action on glucose transportin the isolated rat adipose cellff Apparent translocation of intracellular transportsystems to the plasma membrane. Diabetes 41: 1320–1327.Ĭhen L, Alam T, Johnson JH, Hughes S, Newgard CB, Unger RH (1990) Regulation ofbeta-cell glucose trasporter gene expression. J Biol Chem 265: 7994–8000.Ĭhen C, Thorens B, Bonner Weir S, Weir GC, Leahy JL (1992) Recovery of glucose-inducedinsulin secretion in a rat model of NIDDM is not accompanied by return of the B-cellGLUT2 glucose trasporter.
J Biol Chem 267: 14523–14526.Ĭharron MJ, Kahn BB (1990) Divergent molecular mechanisms for insulin-resistant glucosetransport in muscle and adipose cells in vivo. Diabetes 43: 976–983.īurant CF, Takeda J, Brot Laroche E, Bell GI, Davidson NO (1992) Fructose transporter inhuman spermatozoa and small intestine is GLUT5.

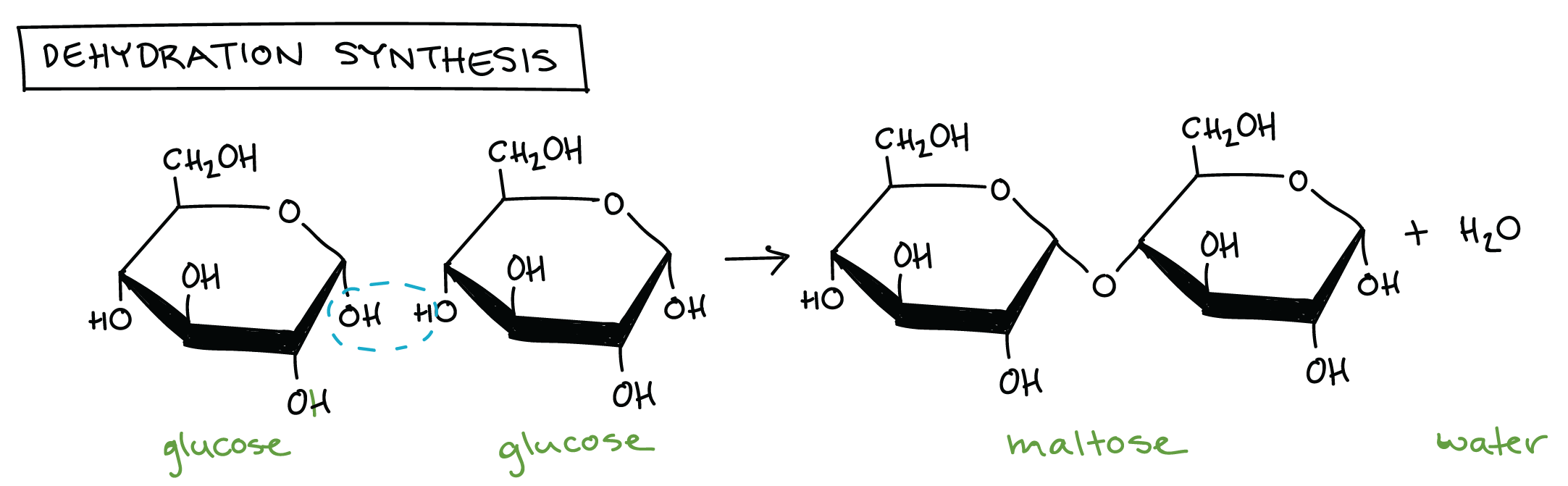
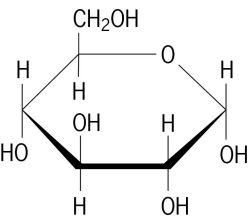
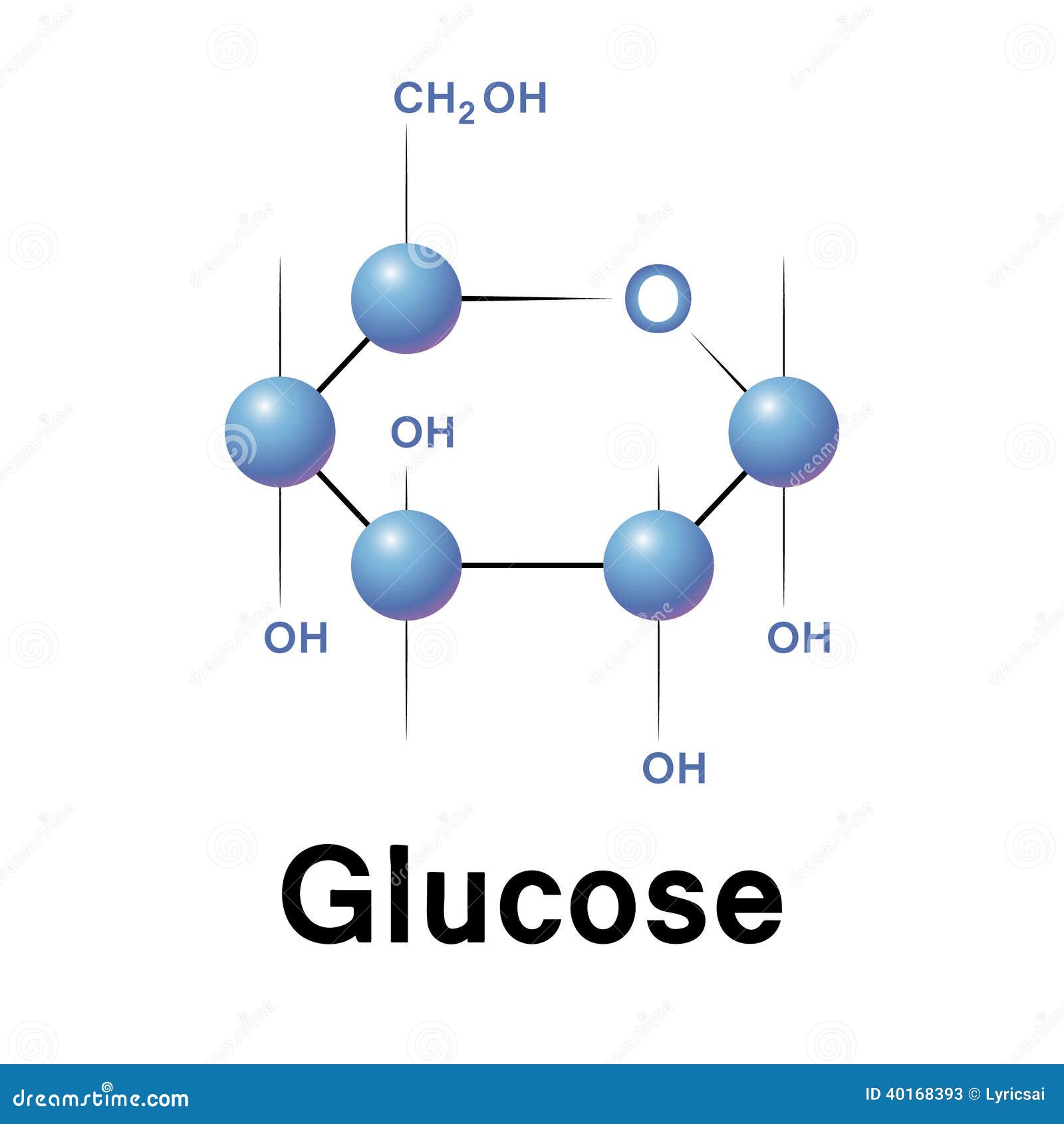
Deficiency of the secondary active sodium/glucose transporters result in glucose/galactose malabsorption or congenital renal glycosuriäGLUT1 deficiency produces a seizure disorder with low glucose concentration in cerebrospinal fluid and GLUT2 deficiency is the basis of the Fanconi–Bickel syndrome, which resembles type I glycogen storage disease.ījorbaek C, Echwald SM, Hubricht P, et al (1994) Genetic variants in promoters and codingregions of the muscle glycogen synthase and the insulin-responsive GLUT4 genes in NIDDM. Primary defects in glucose transport all appear to be extremely rare and not all possible deficiencies have been identified. The pattern of expression of the GLUT transporters in different tissues is related to the different roles of glucose metabolism in different tissues. In all other cells, glucose transport is mediated by one or more of the members of the closely related GLUT family of glucose transporters. In the intestine and renal proximal tubule, glucose is transported against a concentration gradient by a secondary active transport mechanism in which glucose is cotransported with sodium ions. There are two mechanisms for glucose transport across cell membranes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
